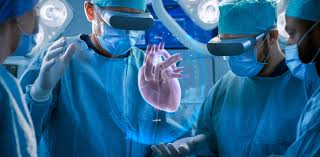
Virtual reality (VR) is no longer just for gaming—it’s transforming the operating room. Surgeons now use VR technology to plan procedures, train medical staff, and even perform complex surgeries with enhanced precision and safety.
1. What VR Brings to Surgery
Virtual reality creates immersive, 3D environments that simulate the human body and surgical scenarios. Key applications include:
- Preoperative planning: Surgeons can explore a patient’s anatomy in 3D before making the first incision.
- Training and simulation: VR provides risk-free practice for medical students and specialists.
- Remote assistance: Surgeons can collaborate or guide procedures from anywhere in the world.
- Patient education: VR helps patients understand complex procedures and recovery processes.
By combining visualization, simulation, and interactivity, VR enhances surgical precision and outcomes.
2. Benefits of VR in Surgery
- Improved accuracy: Surgeons can rehearse complicated procedures, reducing errors.
- Faster learning: Medical students gain hands-on experience without putting patients at risk.
- Reduced operation time: Pre-planning and guidance shorten surgeries, improving efficiency.
- Enhanced patient safety: Virtual simulations allow teams to anticipate challenges before entering the OR.
- Remote surgeries: VR enables tele-surgery, making expert care accessible worldwide.
3. Real-World Applications
- Orthopedic surgery: VR helps map bones and joints for joint replacements.
- Neurosurgery: Surgeons navigate complex brain structures with VR guidance.
- Cardiovascular procedures: VR assists in planning stent placements and other interventions.
- Medical training programs: VR simulators allow residents to practice thousands of procedures safely.
These examples show how VR is integrating into everyday surgical practice.
4. Challenges and Considerations
- High costs: VR systems require investment in hardware, software, and training.
- Technical limitations: Realistic simulations require high-resolution imaging and processing power.
- Adoption barriers: Surgeons and hospitals may resist adopting new technologies.
- Integration with existing workflows: VR must complement, not disrupt, established surgical protocols.
5. The Future of VR in Surgery
Advances in VR combined with artificial intelligence, haptic feedback, and augmented reality (AR) could make surgery:
- Even more precise, with real-time tissue analysis.
- Collaborative, allowing multiple surgeons to operate in shared virtual spaces.
- Personalized, adapting procedures to individual patient anatomy in real time.
Eventually, VR may become a standard tool in every operating room, improving outcomes and accessibility of healthcare worldwide.
Final Thoughts
Virtual reality is redefining surgery, bridging the gap between planning and practice, and providing surgeons with tools to operate with unprecedented accuracy. By combining immersive technology and real-time data, VR is enhancing patient care and shaping the future of medicine.